Code-Required Minimum R-Values
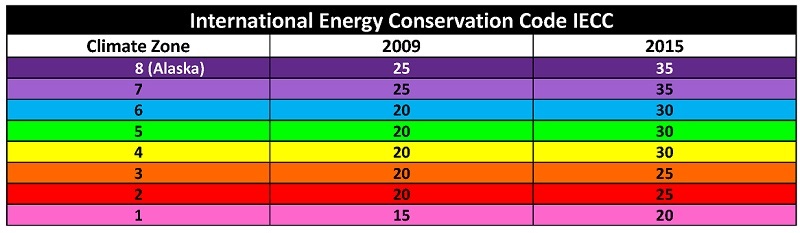
Over the past 10 years, there has been a shift in minimum required R-values. The 2015 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) is the driving force behind this movement. More than 20 states have adopted the 2015 IECC, or a portion of its provisions, as their statewide energy code. See the chart below for minimum R-values per climate zone.
Since 2009, the roofing industry has seen an R-10 increase in the majority of the states. The total minimum insulation thickness has increased from 3.5" (R-20) to 5.2" (R-30) in parts of over 40 states. The map below can help you identify climate zones within your state. Climate zones 4 through 8 have experienced an R-10 increase.
Additional resources are provided below to help you determine the applicable energy code and its associated minimum R-value requirements in a given state or local jurisdiction.
- Minimum Insulation R-value Requirements: Non-Residential, Above Roof Deck
- The Building Codes Assistance Project
Up Next
Polyiso Storage, Handling, and Application Guidelines
Wet insulation can lead to several issues including mold, reduced membrane adhesion, and ultimately roof system failure during wind events.
CAV-GRIP III in Cold Weather: Best Practices
For many contractors, the onset of cold weather means delayed progress, but that mentality is changing.
Installation Tips for Pressure-Sensitive Elastoform Products
Heat exposure is what causes Pressure-Sensitive Elastoform Flashing® (PSEF) to cure on the roof after installation...